Comparative Analysis of Linear Discriminant Algorithms and Support Vector Machine in Palm Fruit Image Disease Classification
Keywords:
Image Classification, Palm Fruit, Linear Discriminant Analysis, Support Vector Machine, Cross ValidationAbstract
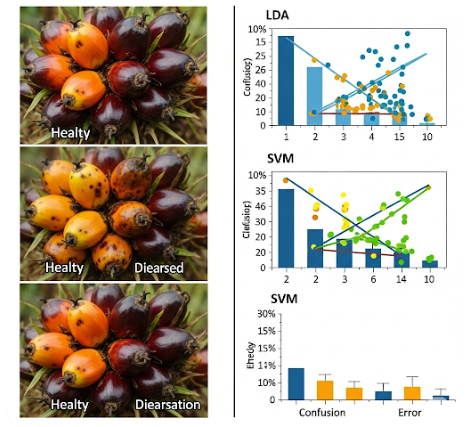
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer vision used for object detection and image classification using algorithms. Approaches to comparing object characteristics in image processing can be divided into High Dimensional Feature approaches and Low Dimensional Feature approaches. Support Vector Machine (SVM) is an accurate High Dimensional Feature method, while Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is a powerful Low Dimensional Feature Method. Some studies combine SVM with LDA to reduce complexity and improve performance. In the classification of palm fruit disease images, the comparison between SVM (High Dimensional Feature) and LDA (Low Dimensional Feature) can be made with variations in dataset size and the percentage of training and testing data in the research is 50:50, 60:40, and 70:30. Performance measurement is based on accuracy, precision, recall, and f-1 score. The algorithm for testing predictions for the validity of accuracy results is k=5 Cross-Validation. The average test results in Linear Discriminant Analysis had the highest prediction, namely 86.00%, obtained in the 1st iteration, a percentage of variation of 50% of the image data. Meanwhile, the lowest average value was obtained in the 5th iteration, namely 66.00%, a percentage of variation in 30% of the image data. Then the average prediction value for system testing is 79.67%. Meanwhile, the support vector machine calculation test results have the highest prediction average, namely 96.00%, obtained in the 1st iteration, a percentage of variation of 30% of the image data. The lowest average accuracy value was obtained in the 1st iteration, namely 92.55% with a variation percentage of 40% of the image data. Then the prediction value for the test data system was obtained at 93.98% of the average results for each iteration. This study aims to compare the performance of LDA and SVM algorithms in classifying healthy or diseased oil palm fruit with variations in data set size and percentage of training and testing data. From the results of research testing, SVM has an accuracy of 93.33% at the 1st percentage variation. Meanwhile, LDA is 86.66% with the same percentage variation. SVM was shown to be more effective in classifying images of sick palm fruit or healthy fruit compared to LDA.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Sociology of Religion

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


